English translation of preprints prepared for ENAA/JPMF PM Symposium '99 held in May 19, 1999
Engineering, procurement and construction (hereinafter called EPC) contractors for process industry allocate their resources for multiple projects awarded by their clients. In PMBOK, program is defined as a group of projects managed in a coordinated way to obtain benefit not available from managing them individually. In this sense, EPC contractors are managing a program of their own.
When supply and demand balance of the plant market shift in over supply side, importance of a program management will be soon realized. Because the contractor's risk of the fixed price contract projects increases in such environment. In the early stage, contractor will try to minimize cost by all means such as Just-in-time (JIT) construction or construction driven engineering and procurement, concurrent engineering, performance type specification, supply chain management etc. But as the market price goes down beyond certain limit, i.e. threshold value, cost overrun risks is heightened and many project end up with deficit.
Thus early detection of the threshold value becomes very important for the contractor. Author proposes to break down the work to accountable work package and assign accountable person for each work package and ask them to find out threshold value for each division of the work.
EPC contractors who supply processing plant for the industry are engaged in many projects simultaneously. Value of contractors for the society lies in the capability for sharing resources such as human, knowledge, skills, equipment and facilities among those various projects thus enhancing overall social efficiency.
According to the text book of Project Management Institute (PMI), i.e. Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), program is defined as a group of projects managed in a coordinated way to obtain benefit not available from managing them individually. In this sense EPC contractor is managing the Program of its own. Because they have to enhance its own efficiency in such a manner to nicely allocate its resources.
Demand for the plant construction market changes depending on industry needs. When the market goes into over supply mode, price level of fixed price contract market goes down. In this mode, contractor has to concentrate in program management to minimize the risk of cost overrun of the fixed price contract. Because it is contractors responsibility to take risk of the cost when baseline (or scope of work) of the contract remain the same.
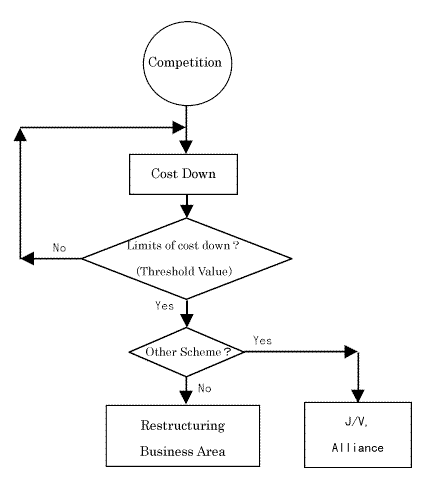
When the plant market enters over supply mode, number of projects for the contractor decreases. To maintain workload, contractor has to either lower offer price or make alliance with his competitor. When he fail doing so, he has to reduce work forces from this business domain.
At the initial phase of over supply mode, contractors try to lower its cost. But it is impossible to continue reducing the cost forever. Some times, the market price reaches certain point from which cost reduction is extremely difficult. Let's call this limit as threshold value. Any people or organization or project has different threshold value. Even themselves does not know the figures. It gradually becomes apparent along the progress of the project. When the market price continue falling and exceed the threshold value, risks of cost overrun increases. The threshold value also continues falling because cost reduction effort continues.
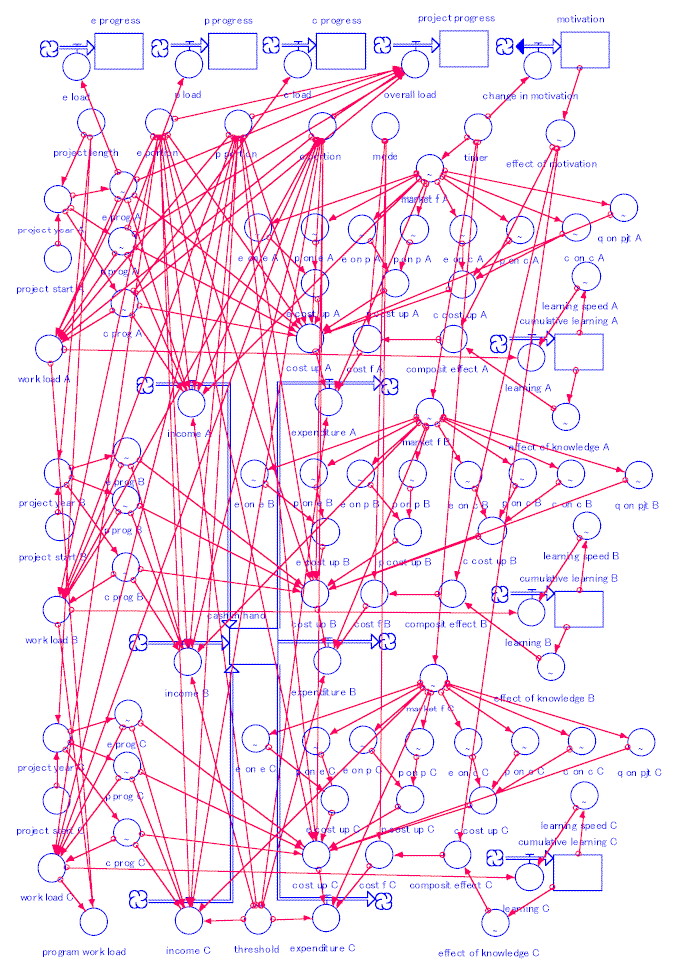
In this context, program management means a series of activities ranging from cost reduction, finding discrepancies between market price and saturated cost or threshold value and take necessary action of resource dislocation from targeted market domain. This whole process is illustrated in Fig.-1

In this article, discussion will follow like; Why plant owner prefers fixed price contract? What contractor should do before signing contract agreement? How to make cost reduction during project execution?
The result of cash flow simulation at a time when the market price exceeded the threshold value. The objective of the article is to propose the method of finding the timing when market price exceeded the threshold value.
There are 4 types of contract agreements between owner and contractor. Those are:
(1) Reimbursable contract
(2) Fixed price contract
(3) Stepwise fixed price contract
(4) Client alliance contract
Reimbursable contract is a main stream in petroleum and chemical industries in Europe and USA where plant owner has basic technology and confidence in project execution. It is not necessary to establish firm baseline before signing contract agreement. Evergreen contract and framework contract may be a variation of reimbursable contract. evergreen contract fixes only unit manpower cost over certain period. Frame work contract measures performance of contractor periodically. All project risks are bone by owner.
Fixed price contract was commonly adopted for simple process such as power plant. Owner relies on contractor who has technology and capability of designing plant and executing the project. Even in USA, most of the power plant project uses this agreement. Contractor can take risks because power plant is simple. But in Asia, this fixed price agreement is common even in complex process plant. In Asia, plant owner has no technology and they have to rely on contractor to take risks. Japan is no exception. Historically in Japan, most plant owner started business by introducing foreign technologies. All cost risk during EPC stage by contractor. But Life cycle cost is owner's risk.
Stepwise fixed price contract is a combination of reimbursable contract and fixed price contract where project starts with reimbursable contract and convert to fixed price contract when baseline becomes clear to both parties. In the end, risks are shared among owner and contractor. Problem for owner is the difficulty of selecting contractor.
There are many variations in client alliance contract. Incentive contract or profit loss sharing contract is one of client alliance contract. Major plant owner is seriously considering client alliance contract to offset higher lifecycle cost typically seen in fixed price contract. Risks during EPC phase are born jointly by owner and contractor. Owner needs a supervising power.
Recent trend in fierce global competition is that contractor to accept fixed price contract and to take full risks during EPC phase.
Fixed price contract assumes that baseline of the contract is firm and all cost are included in its contract price. But when supply capacity is exceeding demand, definition of baseline is simplified in away to define performance only. Because of lack of cash flow due to fierce global competition, plant owners are forced to cut budget for baseline definition work, .
In these circumstance, owner's project department was downsized and the front end engineering and design (FEED) or front end loading (FEL) work is outsourced. Historically, owner normally did it. Consultant selection is also done by competitive bidding with the condition of fixed price contract agreement.
To accomplish contractual requirement of FEED or FEL work, consultant has to adopt strategy to minimize their cost by defining performance requirement instead of providing detailed specification.
For EPC contractor, performance type baseline does not contain sufficient information for their cost estimate. Never the less, time given to contractor for their bid preparation is short. Thus cost estimation becomes very crude. If contractor put high contingency, they tend to loose the job. The pressure to cut contingency becomes enormous.
Even if enough time is given to the contractor, it is a waste of effort for all contractors to do FEED work for their estimate. Eventually, all duplicate FEED cost required to make estimation becomes owner's cost.
Fixed price contract is not the best mechanism to avoid duplicate effort of FEED work and risks inherent in fixed price contract. Contractual scheme other than fixed price contract shall be considered. But fixed price contract is still most favored scheme by weak owner who has less experience in plant construction.
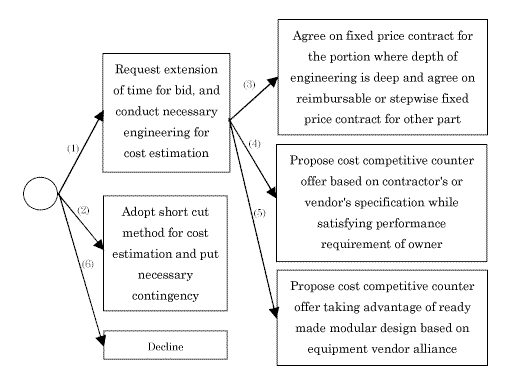
As shown in Figure-2, there are two routes to avoid risks in cost estimation.
(1) Request extension of time for bid, and conduct necessary engineering for cost estimation.
(2) Adopt short cut method for cost estimation and put necessary contingency in their estimate.
Selecting second route is very speculative. Too many contingencies mean a loss of project and small contingency result in cost overrun. Contractor who is working on several projects can lump up all projects and makes even profit out of all. But this method is not applicable to big project.
Selecting the first route is also not easy under fierce competition. Considered sub-routes of the route (1) are:
(3) Agree on fixed price contract for the portion where depth of engineering is deep and agree on reimbursable or stepwise fixed price contract for other part
(4) Propose cost competitive counter offer based on contractor's or vendor's specification while satisfying performance requirement of owner.
(5) Propose cost competitive counter offer taking advantage of ready made modular design based on equipment vendor alliance.
Sub route (4) and (5) could not be implemented by single project, because they are similar to the idea of platform concept of automobile industry. Only program management can achieve such idea. In all cases, owners should have a brief that alternative may have something new to the industry and may bring breakthrough.
When all fails, contractor has decline from bidding.
In 1996, Construction Industries Institute (CII) proposed a new Project Definition Rating Index (PDRI) which can measure the depth of FEED or FEL. This method measures the depth of engineering in each category and weighted average value is regarded as an indicator of the depth of FEED. This method is considered to take time and produce nothing, but without quantitative indicator, any organization could not make right decision.
Regardless the route, in actual execution of the project any criteria taken should be reassessed to modify criteria for future decision.
Traditionally, under the common-law, when conflict arises between owner and contractor about the baseline of the contract, so called contra proferentem rule is applied. But recently, notorious exculpatory clauses are included in the agreement. This clauses request contractor to include all cost in to its estimate that covers all potential risks and agrees that he takes all liabilities. Once common-law has a doctrine that suppresses unreasonable exculpatory clauses but this doctrine lost effectiveness by recent judicial precedents.
Project managers and program managers should have full knowledge of those legal trends and make decision accordingly.
Simple cost competition should be avoided. Instead, more creative approach to the project may be required to avoid risks associated with cost competition.
Author will not discuss currency exchange risks.
After agreeing fixed price contract, project manager has to complete the project within agreed contract price while keeping the quality of work. It is a difficult job when market price is falling down due to fierce competition.
Typical cost beak down of the plant construction project is shown in Table-1.
Cost Item |
Percentage of Cost (%) |
Engineering |
20-15 |
Procurement |
40-60 |
Construction |
40-25 |
It is apparent that relative cost of procurement among total project cost is the highest and construction cost follows. Engineering cost is the lowest. Higher the relative cost, it is more effective for cost reduction. Detail of cost reduction will be discussed in the following paragraphs.
Procurement activities include purchasing equipment materials from vendors and construction services from construction subcontractors.
Procurement volume reduction by constructability approach will be discussed later.
As procurement cost reduction is so effective that best personnel should be appointed to procurement services. Procurement strategy should be controlled on program management level and not on project level.
Purchaser should be a professional who has full knowledge of purchasing objects i.e. equipment and materials, vendors, services, subcontractors and the market. He should be a man who can create a new relationship with providers in a creative manner. For example, new scheme of risk sharing among purchaser and suppliers may be possible.
In engineering, preparation of a simple and firm specification without any change is desirable. Sometimes, it may be necessary to provide fabrication drawings and or materials for weak fabricator.
Contractual terms and condition among purchaser and supplies is one of the most cost-effective elements. Bearing all risk by supply side results in excessive contingency cost and bearing all cost by purchasing side results in lack of effort in supply side. There lays optimum scheme. There are 4 types of contractual relations.
(1) Reimbursable contract or unit price contract
(2) Fixed price contract
(3) Stepwise fixed price contract
(4) Vendor subcontractor alliance contract
Reimbursable contract or unit price contract is applied to construction work where baseline is not fixed yet or to bulk material where quantities are not fixed yet. Fixed price contract or purchase agreement is applied to equipment. Stepwise fixed price contract is recommended for construction contract.
There are 3 ways in selecting vendor and contractor.
(a) Open bid
(b) Bid by nominated suppliers
(c) Optional contract
Open bid is not common in EPC business. There are several reasons for this. Those are needs for quality and secrecy reason of technical know how. In addition, numbers of suppliers are limited anyway. But selection of bulk material vendor may go into open bid through Internet.
Bid by nominated suppliers is the most common way. Several bidders are selected after accessing technical capability, ability to keep delivery time, logistic advantage etc. and ask them to bid.
Competitive bidding has advantage over other method. Because it can reduce procurement cost. But it has also disadvantage. Many vendors spend certain cost for preparation of bid and most of them loose without direct compensation of the cost. But contractor is paying this cost indirectly.
To avoid such inefficiency, optional contract or creation of cooperative supply chain would be an alternative route. This method has been applied to bulk materials but it could be used for cost reduction of equipment cost by face to face communication between vendor and purchaser. Cooperative supply chain becomes very powerful when route (4) or (5) of Fig-2 is selected. Only problem would be how to reflect market price level. One way is to deduct savings by alliance from market price.
Construction cost reduction is second effective means of cutting cost after procurement cost reduction.
Work volume reduction by constructability approach will be discussed later.
Block construction developed by ship building industry for cutting construction cost may also be one of costructability concept. I would like to use the terminology "block construction" to cover all pre-assembling activities such as piping and steel structure prefabrication, modularization, skid mounting and dressing up of columns.
There are many variations in a block construction. Most suitable method is applied to meet the special characteristics of the site such as labor cost, availability of construction equipment, tools and scaffoldings.
The purpose of block construction is to minimize field construction activities and to shave off peak load at the field. When peak load is shaved off, it reduces cost and minimizes complexities at the field. On the other hand, block construction needs heavy cargo handling equipment and time for module construction. It is needed to solve trade off among advantage and disadvantage of the method.
Regardless the construction method applied, all deliverables such as modules, equipment, materials, drawings, labor, construction equipment, tools and scaffoldings shall be at the site at the right time. If timing is not correct, many waste of work and waste of material such as, idle of work force, rework, double investment for construction infrastructure are caused and result in cost over run and delay of work.
To achieve Just-in-Time (JIT) arrival of deliverables to construction site, well planned engineering plays the key role. I may call it construction driven engineering, or JIT construction.
In JIT construction, construction method is selected before starting engineering and procurement activities. Then time of arrival of deliverables to construction site is determined for the selected construction method.
Early arrival of deliverables that result in storage area shall be avoided. Temporary storage management system becomes heavy and loss may be caused. To avoid this situation, incentive and penalty clause has to be built in the agreement with supplier.
Dilemma in JIT construction is construction method could not be finalized before design of equipment and selection of equipment vendor. Once construction method is finalized then it is easy to select appropriate vendor considering Trans- shipment to the module construction site.
To minimize rework in construction site, sometimes, rework in engineering is unavoidable. In any case, sequential processing in engineering is no longer possible. To achieve JIT construction, concurrent engineering is more than necessity.
Full utilization of advanced communication system between engineering office and construction site is mandatory.
Relative cost of engineering in total project cost is smaller than other activities of the project. Therefore, engineering cost reduction is not so important. Rather, overall cost reduction is bigger when spending more in engineering. Eventually, it can expect saving in down stream. In other words, to achieve JIT construction, concurrent engineering is more important in cost reduction.
I would like to site a few example.
(1) Equipment layout which minimize piping material
(2) Underground piping system design, which minimize excavation work volume
Equipment layout that minimizes piping material is now possible by advanced oftware for automatic 3 dimensional (3D) piping routing.
By putting drainage pump station at shorter intervals, depth of drainage piping becomes shallow. Thus overall excavation work volume becomes smaller.
In both case, big cost saving in procurement and construction will be achieved by small addition of engineering cost.
In a small project, a single person who knows every thing from design to construction can make decision in the right time and supervise the project. He is a kind of superman. But for big project, it is almost impossible to find such person.
Concurrent engineering defined by IDA (Insutitute for Defence Analysis) report R-338 published in 1986 was an answer to supersede the superman. In concurrent engineering, sharing information among the parties including all spectrum relating the life cycle of the products and conducting the work in emergent (the word was borrowed from chaos theory and added by author) manner are the key to the success of the project.
In a small project, people can sit in the same room and conduct concurrent engineering with face to face communication. I call it "physical single room" project. But in a big project, it is impossible that all people sit in the same room. If all functional people sit in the same room, deciplinary capability also degrades. EPC contractor's value lies in program management by taking advantage of time sharing of their core personnel. Matrix organization was invented for this purpose.
Electronic communication tools are helping people to make communication easy thus creating "virtual single room". E-mail system is one of the elements of "virtual single room". But it is not enough. The 3D model of the plant stored in an electrical filing system shall be accessible by all parties. It will enable real information sharing among individuals constituting project team. Combined with the information sharing tools for concurrent engineering and project control systems, field rework was reduced from over 10% down to 4%.
Technological development will continue, but key point is that it is people who use it. "Virtual single room" will evolve, but still face to face communication is far superior than electrical system. Management by walking around (MBWA) will still dominate.
Once all 3D plant model is stored in electrical filing system, sub-route (5) of Fig-2 " propose cost competitive counter offer taking advantage of ready made modular design based on equipment vendor alliance" becomes very strong weapon in EPC industry. It may change the paradigm of the business.
To achieve JIT construction, all engineers, vendors and transporters have to know their schedules. Not only knowing, schedule information sharing system has to provide means of collecting current status and adjusting schedule in emergent manner.
Author did a numerical simulation to know what will happen when market price is below threshold value. In this chapter, assumptions and result will be discussed.
Scenario of the simulation was set as follows:
When market goes into a falling price mode (D), as a first reaction, EPC contractor tries to follow this trend and lowers their offer price. As far as supply capacity is exceeding demand, this trend continues and market price continues falling. With all effort of reducing their cost, eventually market price becomes lower than threshold value and risk of cost over run becomes enormous.
Normally, it takes some time before engineering and procurement risks show up as real loss in construction phase, because duration of big project takes about 3 years.
If market price continuously drops 10% in each year, after 3 years, market price becomes 70% of threshold value. If all parties in the market realize that market price is below threshold value, then they stop joining the market. At this moment, market price start bouncing again or enter in a rising price mode (U).
Even in rising price mode, the market price never return to threshold value stepwise because no body know threshold value and market has momentum.
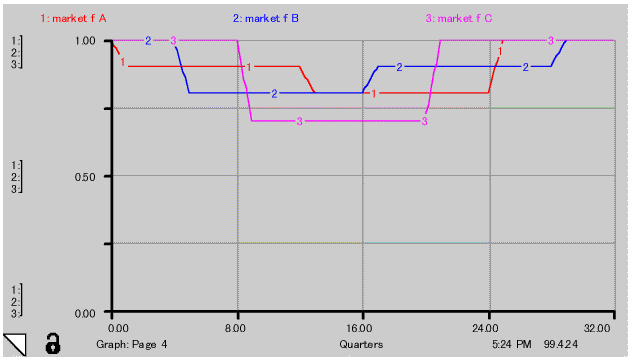
When program is divided equally in 3 project line, namely, Project A Line, B Line and C Line, Project budget of each line follows market factor of project award time. It is illustrated in Table-2.
Year |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
Quarter |
0 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
32 |
Market Factor on Threshold |
0.9 |
0.8 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
0.9 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
Mode |
D |
D |
D |
U |
U |
U |
E |
E |
E |
Budget of Project A Line |
0.9 |
0.9 |
0.9 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
Budget of Project B Line |
1.0 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.9 |
0.9 |
0.9 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
Budget of Project C Line |
1.0 |
1.0 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
After entering rising price mode, another 5 years are required to complete all projects awarded before entering rising price mode.
Assuming that threshold value is constant, cumulative profit and loss value will be calculated. In this case, after market returned to normal, cumulative loss remains forever.
Assuming that threshold value could be improved about 10% by composite effect of motivation and learning, cumulative profit and loss value will be calculated. In this case, after market returned to normal, cumulative loss may be offset by profit earned by improved threshold value.
In this simulation, cost incurred for bid preparation and corporate overheads were not included in simulation.
It is assumed that:
(1) Simulation starts when market price becomes lower than threshold value.
(2) Duration of all projects are 3 years.
(3) During falling price mode, project budgets are:
(4) During rising price mode, projects budget are:
(5) Project budget never changes until its completion. Project budget of each project line that was determined by market factors are shown in Fig.-3.
(6) Risks on each activity will be defined by percentage as shown below:
(7) Cost up of each EPC activities are calculated by following equations.
E Cost up = (1+(E on E)/100) x (1+(P on E)/100)
P Cost up = (1+(E on P)/100) x (1+(P on P)/100)
C Cost up = (1+(E on C)/100) x (1+(P on C)/100) x (1+(C on C)/100)
Cost up of each EPC activities will be allocated according to the EPC load curve.
(8) Cost break down of EPC activities are:
(9) Quality degradation will increase cost evenly throughout the project.
Project Cost up = (1+ (Q on Project) /100) x
(0.15 x (E Cost up)+ 0.6 x (P Cost up) + 0.25 x (C Cost up) )
(10) Based on equations in (7) and (9), risks and cost up of each EPC activities are calculated as shown in Table-3.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As you can see in Table-3, even if individual risk figures are small, composite risk becomes enormous. Functional engineers assigned for engineering phase can only detect risks such as E on E, E on P, E on C and P on E. They could not realize composite risks which sum up to 17 %. Potential dangers are that composite risks are hidden to functional engineers.
(11) All project follow EPC loads curve as shown in Fig.-4. Project overall load curve is calculated from individual load curve by applying cost break down of EPC activities shown in (8).
Fig.-4 EPC Load Curve
Project control activities are included in engineering.
When load curve is integrated, progress curve or S-curve will be obtained. This is shown in Fig.-5.
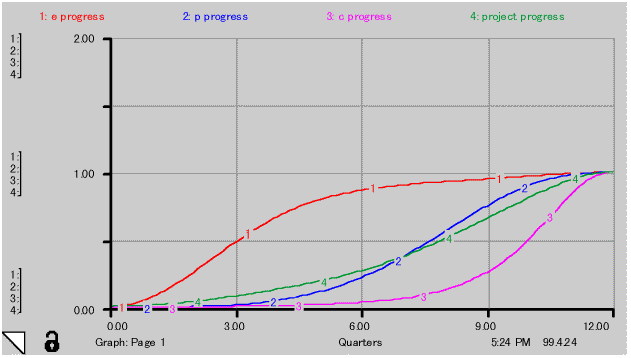
Cumulative profit and loss at constant threshold value was calculated. Specific assumptions made for this case are:
(1) Annual turn around of 3 billion US$.
(2) Payment by client follows EPC load curve as defined in Fig.-4 and cost break down of EPC as defined in (8) of para.5.2
(3) Payment by project is equal to payment by client as described in (2) plus EPC cost up calculated using EPC risks and quality degradation risks listed in Table-3.
(4) Threshold value does not change over 8 years.
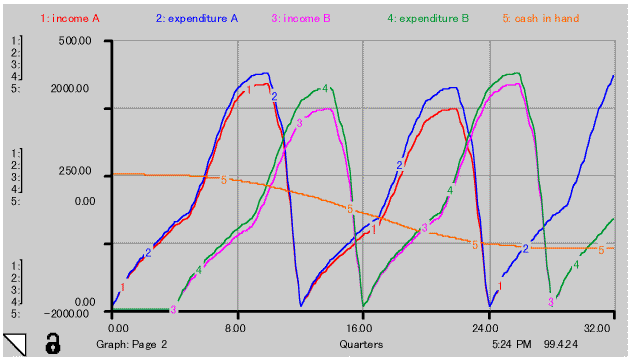
Cumulative profit and loss is shown in Fig.-6 curve 5 as cash in hand. Corresponding project cash flows are shown in curve 1 to 4. No substantial change of cash in hand appears over 2 years. A loss of 1.2 billion US $ remains.
Cumulative profit and loss at improved threshold value was calculated. Specific assumptions made for this case are:
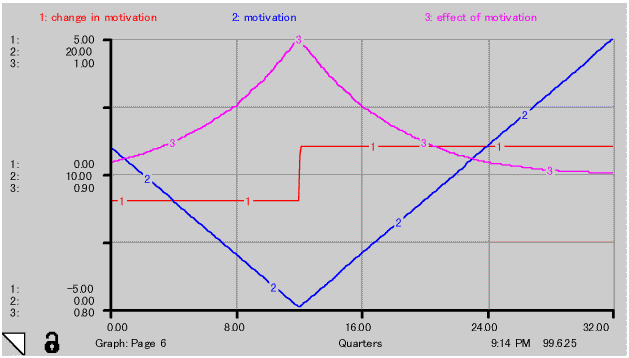
(1) Maximum figure of cost down factor achievable in 8 years is 10% of threshold value. Cost down factor is a composite of motivation and cumulation of knowledge by learning.
(2) During falling price mode, motivation falls and during rising price mode, motivation is enhanced. This effect on cost down factor is shown in Fig.-7.
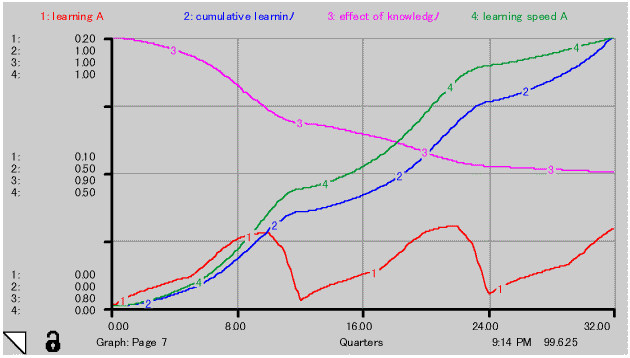
(3) Learning is proportional to work load. Learning speed is proportional to cumulative learning. Rate of learning speed is 10% of cumulative learning. Typical example of effect of knowledge on cost down factor of project A line is illustrated in Fig.-8. Effect of knowledge saturate gradually along accumulation of learning
(4) Cost down factor is a composite 20% of the effect of motivation and 80% of effect of knowledge. This is shown in Fig.-9.
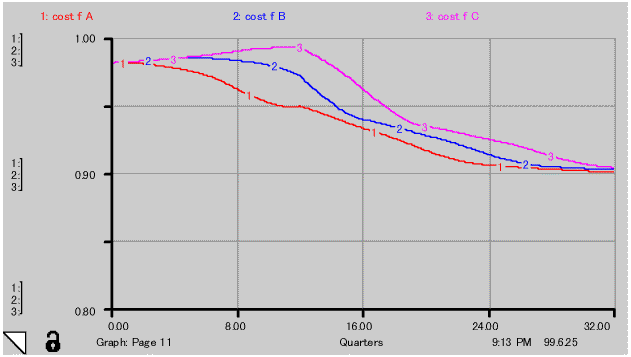
(5) Risks and cost up of each EPC activities listed in Table-3 are applicable.
Cumulative profit and loss is shown in Fig.-10 curve 5 as cash in hand. Corresponding project cash flows are shown in curve 1 to 4. No substantial change of cash in hand appears over 2 years. Maximum loss of 0.5 billion US $ was offset by profit earned by improved threshold value over 8 years.
Change of weighting factor on effect of motivation and effect of knowledge has no substantial impact.
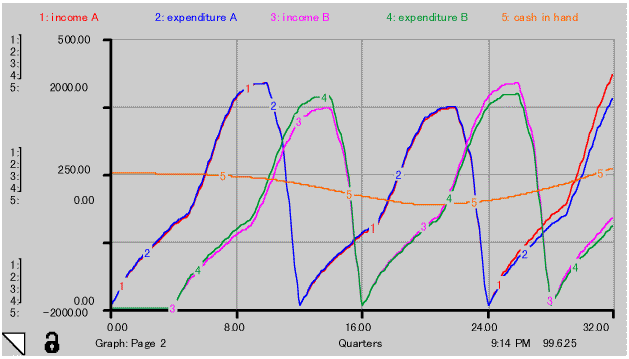
As explained in paragaraph 1, any people or organization or project has different threshold value. Even themselves does not know the figures. It gradually becomes apparent along the progress of the project.
It takes about 2 years before stakeholders realizes that project budget is below threshold value. After 2 years, cumulative profit and loss starts to overshoot. Because during initial stage, no action is taken and strategy of program management keeps saying, "cost reduction". In the past, the phenomena were repeated in every 10 years. This cyclic oscillation is caused by distance-velocity lag as defined in Process Control Theory.
It is said that most important characteristic of project manager is the ability to find risks and bottlenecks. The same applies to program manager. But relying only on individual is a fragile system. Mechanisms of finding risk should be build in the system.
As shown in Fig.-11 that was copied from BS 7000 design management system, cost is committed by design. Actual spending comes later. Cumulative profit and losses are reflecting only costs actually spend.
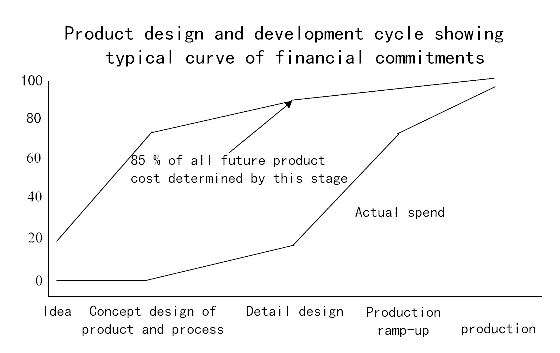
Early detection of saturation of cost reduction is how to reflect cost committed by design.
Earned Value Management Technique (EVMT or EVMS) or DoD Instruction 7000.2,"Performance Measurement for Selected Acquisitions" has a potential for inclusion of the cost committed by design. EVMS methodology may be an answer to the early detection of saturation of cost reduction. EVMS is a costly system, but risk money is bigger than cost for EVMS.
BS6079 project management defines how to breakdown the work into accountable work package.
I would like to propose to breakdown the work into accountable work package and assign accountable people and monitor cost and schedule simultaneously by EVMS.
Combination of BS 7000, BS6079 , EVMS and MBWA will assure early detection of saturation of cost reduction.
I wish to acknowledge the many comments rendered to me from my colleagues and friends. I also appreciate permission given by my company for presenting ENAA/JPMF Symposium 99.
(1) Wayne F. Abba, "Beyond Communication with Earned Value", PMI 26th Annual Seminar/Symposium 1995
(2) Wayne F. Abba, " Earned Value Management", PMI 27th Annual Seminar/Symposium 1996
This is an English translation of preprints prepared for ENAA/JPMF Symposium '99 held in May 19, 1999. Some modification were added after Symposium.
The model diagram made by iThink (Stella) developed by High Performance Systems Inc. This software is a similar one to Dynamo used for famous book published in 1972, "The Limits to Growth" by Club of Rome.