☆Cocoa Foundationクラス(等)勉強室3
セット(重複排除配列);NSSet/NSMutableSet/NSCountedSet
NSSet/NSMutableSetは配列の一種である。が、NSArray/NSMutableArrayとの最大の違いは、 「要素の重複を許さなくすることができる」と「速い」ことにある。
NSSetは、要素(idで表せるクラスオブジェクト)に対してisEqual:メソッドを投げる。 isEqual:メソッドは一番親のクラスであるNSObjectで定義されているので、よほど特殊なクラスを使わない限り 必ず持っている。要素を示すクラスのisEqual:メソッドをオーバーライドしておくのである。 YESを返すと、重複があるの印になる。
isEqual:メソッドは以下のように実装するらしい。
-(BOOL)isEqual:(id)other
{
if (other == self) { // 自分自身の時は当然一致
return(YES);
}
if (other ==nil) { // nilの時は何者とも一致しない
return(NO);
}
if (![other isKindOfClass:[self class]]) { // クラスが異なる
return(NO);
}
// 内容の固有の比較式
// if(![クラス名 isEqualToString:[other valueForKey:@"文字列"]]){ とか
// if (_window_id != [anObject windowID]) { とか
if (不一致) {
return(NO);
}
// 一致
return(YES);
}
isEqualはデフォルトでは「アドレス比較」なので不一致はともかく、内容一致判定には向かない。
従って、基本的には絶対にオブジェクトに対応した固有の比較式を書く必要がある。
NSSet
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(id)initWithObjects:(id)firstObj ... | 複数オブジェクトでセットを初期化して返す |
| -(id)initWithArray:(NSArray *)array | 配列からセットを初期化して返す |
| -(id)initWithSet:(NSSet *)set | 別のセットでセットを作る |
| +(id)set | 空のセットを作る変更可能なNSMutableSetのために宣言する |
| +(id)setWithObject:(id)object | オブジェクトでセットを作る |
| +(id)setWithArray:(NSArray *)array | 配列からセットを作る |
| +(id)setWithObjects:(id)firstObj ... | 複数オブジェクトでセットを作る |
| +(id)setWithSet:(NSSet *)set | セットからセットを作る |
| -(NSUInteger)count | セットの要素数を返す |
| -(NSArray *)allObjects | セットに含まれる要素のすべてを配列で返す |
| -(id)anyObject | セットに含まれるオブジェクトのうちのどれかを選んで返す |
| -(BOOL)containsObject:(id)anObject | セットにオブジェクトが含まれているかを返す |
| -(void)makeObjectsPerformSelector:(SEL)aSelector | レシーバの要素それぞれにアクションセレクタを実行させる |
| -(void)makeObjectsPerformSelector:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)argument | レシーバの要素それぞれに引数付きでアクションセレクタを実行させる |
| -(NSSet *)setByAddingObject:(id)anObject | 与えられたオブジェクトを追加した新しいセットを返す |
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(id)member:(id)object | セットに指定したオブジェクトがあればそのオブジェクトを返す |
| -(BOOL)isSubsetOfSet:(NSSet *)otherSet | レシーバは他のセット(otherSet)のサブセットかを返す |
| -(BOOL)intersectsSet:(NSSet *)otherSet | レシーバと他のセットの要素のなかで1つ以上同じ要素が含まれているかを返す |
| -(BOOL)isEqualToSet:(NSSet *)otherSet | レシーバと他のセットの内容が同じかを返す;順番は問われない |
以下がNSMutableSet特有のメソッド。
NSMutableSet
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| +(id)setWithCapacity:(NSUInteger)numItems | 変更可能なセットを作る |
| -(id)initWithCapacity:(NSUInteger)numItems | 変更可能なセットオブジェクトを初期化して返す |
| -(void)addObject:(id)object | オブジェクトを追加する |
| -(void)addObjectsFromArray:(NSArray *)array | 配列でオブジェクトを追加する |
| -(void)removeObject:(id)object | 変更可能なセットから指定したオブジェクトを取り除く |
| -(void)removeAllObjects | 全てのオブジェクトを削除して空のセットにする |
| -(void)removeObject:(id)object | 指定したセットのオブジェクトが、レシーバのメンバーのオブジェクトでなければ各オブジェクトを追加する |
| -(void)minusSet:(NSSet *)otherSet | 指定したセットに含まれるオブジェクトを削除する |
| -(void)addObject:(id)object | 指定したセットのメンバーでないオブジェクトをレシーバから削除する |
| -(void)setSet:(NSSet *)otherSet | 他のセットの内容にする |
NSCountedSetはNSMutableSetの子クラスで、重複する要素の追加回数を数えることが出来る。
NSCountedSet
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(void)addObject:(id)anObject | オブジェクトを追加する |
| -(NSUInteger)countForObject:(id)anObject | セット中の指定オブジェクトの追加回数を返す |
| -(id)initWithArray:(NSArray *)anArray | 配列から初期化する |
| -(id)initWithCapacity:(NSUInteger)numItems | 指定された数のオブジェクトを保持するに十分なメモリをもって初期化する |
| -(id)initWithSet:(NSSet *)aSet | Setからcounted setを初期化する |
| -(NSEnumerator *)objectEnumerator | 列挙子を返す |
| -(void)removeObject:(id)anObject | オブジェクトを削除する |
NSSetの一番の使いどころは、画面のタッチ座標を得るイベント処理においてである。
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
// 画面タッチイベントを取得
// Viewを重ねてしまうと(上のViewでも)タッチが受け取れなくなるようである
{
// NSLog(@"touchesBegan=%@",touches);
CGPoint point=[[touches anyObject]locationInView:self];
printOffset(@"point",point);
~
タッチ位置は順番は関係ないし、当然同一座標があってはいけないのでNSSetで送られてくる。
マルチタッチの時は、[touches count]>=2となっている。マルチタッチをサポートするなら、
まずはそれを読み取って処理を変える必要がある。
「セット: 順序立てられてないオブジェクトの集合」も参照のこと。
インデックスパス;NSIndexPath
インデックスパスは、ツリー構造で入れ子にされている複数の配列群の要素番号を通しで管理するものである。 インデックスパス中の個々の要素番号は、ツリーの配列の1要素から他のより深い要素への要素への要素番号を示している。
例えば、
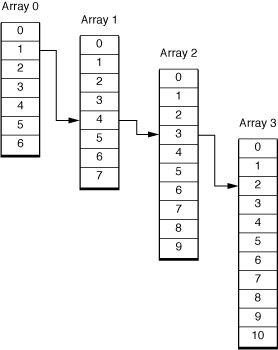 の場合、
インデックスパスは1.4.3.2という。
の場合、
インデックスパスは1.4.3.2という。
別の言い方をすると、正の整数群に特化した配列でもある。 たぶんそう考えた方が理解しやすいと思う。
NSIndexPath
| メソッド名 | 動作 | ||||||
| +(id)indexPathWithIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 1要素でインデックスパスを作成する | ||||||
| -(id)initWithIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 1要素でインデックスパスを作成する | ||||||
| +(id)indexPathWithIndexes:(NSUInteger *)indexes length:(NSUInteger)length | 指定長の要素のインデックスパスを作成する | ||||||
| -(id)initWithIndexes:(NSUInteger *)indexes length:(NSUInteger)length | 指定長のインデックスを初期化し割り当てる | ||||||
| -(NSUInteger)length | 要素数を返す | ||||||
| -(NSUInteger)indexAtPosition:(NSUInteger)node | インデックスパス中のnode番目の要素番号を返す | ||||||
| -(NSIndexPath *)indexPathByAddingIndex:(NSUInteger)index | インデックスパスに要素番号を追加する | ||||||
| -(void)getIndexes:(NSUInteger *)indexes | インデックスパスをindexesに入れる | ||||||
| -(NSIndexPath *)indexPathByRemovingLastIndex | 最後を除いたインデックスパスを返す | ||||||
| -(NSComparisonResult)compare:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath | インデックスパスを比較する
NSComparisonResult(enum値)
|
UIKitを使えるようにしたときには、(カテゴリ)により、 次の プロパティとメソッドが追加される。
UITableViewのアクセスには必須である。
| プロパティ名 | 属性 | 内容 |
| row | R | テーブル・ビューのセクションで行を識別している要素番号 |
| NSUInteger section | R | テーブル・ビューでセクションを識別している要素番号 |
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| +(NSIndexPath *)indexPathForRow:(NSUInteger)row inSection:(NSUInteger)section | 特定の行とセクションのインデックスでテーブル・ビューで初期化されるインデックス-パス・オブジェクトを返す |
「インデックスパス:入れ子になった配列を通したパスを格納する」も参照のこと。
インデックスセット;NSIndexSet/NSMutableIndexSet
NSIndexSetクラスは、不変の一意的な符号なし整数の集合を管理する。 もっと簡単に言えば、配列の中のいくつかの要素番号を選び、それを補助配列として使える機能を提供する。 たとえば、UITableViewの選択中の行の管理などに使う。 ということは「配列の要素番号の集合を扱うクラス」と思って良いはずである。
子クラスにしてはいけないらしい。
NSIndexSet
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(id)initWithIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 要素番号からインデックスセットを作る |
| -(id)initWithIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | 要素番号範囲からインデックスセットを作る |
| -(id)initWithIndexSet:(NSIndexSet *)indexSet | インデックスセットからインデックスセットを作る |
| +(id)indexSet | 空のインデックスセットを作る |
| +(id)indexSetWithIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 要素番号を持つインデックスセットを作る |
| +(id)indexSetWithIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | 要素番号範囲からインデックスセットを作る |
| -(NSUInteger)count | インデックスセット中の要素番号数 |
| -(NSUInteger)countOfIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | 指定範囲内の要素番号数を返す |
| -(NSUInteger)firstIndex | インデックスセット中の最初の要素番号を返す |
| -(BOOL)intersectsIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | インデックスセットが範囲内で要素番号のいずれかを含むかどうか |
| -(BOOL)isEqualToIndexSet:(NSIndexSet *)indexSet | インデックスセットが同じかどうか |
| -(NSUInteger)lastIndex | 最後の要素番号を返す |
| -(BOOL)containsIndex:(NSUInteger)index | インデックスセットが特定の要素番号を含むかどうか示す |
| -(BOOL)containsIndexes:(NSIndexSet *)indexSet | インデックスセットが指定インデックスセットを全て含むかどうか |
| -(BOOL)containsIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | インデックスセットが要素番号範囲によって示される要素番号を含むかどうか |
| -(NSUInteger)getIndexes:(NSUInteger *)indexBuffer maxCount:(NSUInteger)bufferSize inIndexRange:(NSRangePointer)indexRangePointer |
インデックスセットは、インデックス・バッファをインデックスセットと要素番号範囲両方を含む要素番号で埋める コピーした要素番号数を返す |
| -(NSUInteger)indexGreaterThanIndex:(NSUInteger)index | インデックスセット中の指定要素番号より大きい最初の要素番号を返す |
| -(NSUInteger)indexGreaterThanOrEqualToIndex:(NSUInteger)index | インデックスセット中の指定要素番号と同じか大きい最初の要素番号を返す |
| -(NSUInteger)indexLessThanIndex:(NSUInteger)index | インデックスセット中の指定要素番号より小さい最初の要素番号を返す |
| -(NSUInteger)indexLessThanOrEqualToIndex:(NSUInteger)index | インデックスセット中の指定要素番号と同じか小さい最初の要素番号を返す |
NSMutableIndexSet は可変型のIndexSetである。
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(void)addIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 要素番号を追加する |
| -(void)addIndexes:(NSIndexSet *)indexSet | 要素番号群を追加する |
| -(void)addIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | 要素番号群をNSRangeで追加する |
| -(void)removeAllIndexes | 全要素番号を削除する |
| -(void)removeIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 要素番号を削除する |
| -(void)removeIndexes:(NSIndexSet *)indexSet | 要素番号群を削除する |
| -(void)removeIndexesInRange:(NSRange)indexRange | 要素番号群をNSRangeで削除する |
| -(void)shiftIndexesStartingAtIndex:(NSUInteger)startIndex by:(NSInteger)delta | レシーバー内で要素番号群を右または左にずらす |
「インデックスセット: 配列に要素番号を格納すること」も参照のこと。
属性付き文字列;NSAttributedString/NSMutableAttributedString
属性付き文字列は、基本的には文字列にフォント情報を付加した物である。 情報にはフォント種類、大きさ、色などがある。表示用文字列と考えてたらいいだろう。
文字列ではあるが、NSString/NSMutableStringとは全く機能が異なる(NSString/NSMutableStringの子クラスではない)。
NSAttributedString
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(id)initWithAttributedString:(NSAttributedString *)attributedString | 属性付き文字列から属性付き文字列を作って返す |
| -(id)initWithString:(NSString *)aString | 文字列から属性付文字列を初期化して返す |
| -(id)initWithString:(NSString *)aString attributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes | 文字列と文字属性を表す辞書から、属性付き文字列を作って返す |
| -(NSString *)string | 属性付文字列からNSString文字列を得る |
| -(NSUInteger)length | 属性付き文字列の長さを得る |
| -(BOOL)isEqualToAttributedString:(NSAttributedString *)otherString | レーシーバの属性付き文字列と、他の属性付き文字列が同じかを返す |
| -(NSAttributedString *)attributedSubstringFromRange:(NSRange)aRange | レシーバの属性付き文字列から指定した範囲を返す |
NSMutableAttributedString
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| -(NSMutableString *)mutableString | 変更可能属性付き文字列から変更可能文字列を返す |
| -(void)replaceCharactersInRange:(NSRange)aRange withAttributedString:(NSAttributedString *)attributedString | 変更可能属性付き文字列の指定した範囲を属性付き文字列で入れ替る |
| -(void)deleteCharactersInRange:(NSRange)aRange | 変更可能属性付き文字列の指定した範囲を削除する |
| -(void)setAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes range:(NSRange)aRange | 変更可能属性付き文字列の指定した範囲に書体属性を設定する |
| -(void)addAttribute:(NSString *)name value:(id)value range:(NSRange)aRange | 変更可能な属性付き文字列に文字の属性を付加する |
| -(void)addAttributes:(NSDictionary *)attributes range:(NSRange)aRange | 変更可能な属性付き文字列に辞書で文字属性を付加する |
| -(void)removeAttribute:(NSString *)name range:(NSRange)aRange | 変更可能な属性付き文字列にからnameで指定される文字属性を削除する |
| -(void)appendAttributedString:(NSAttributedString *)attributedString | 変更可能な属性付き文字列の末尾に別の属性付き文字列を追加する |
| -(void)insertAttributedString:(NSAttributedString *)attributedString atIndex:(NSUInteger)index | 変更可能な属性付き文字列の番号で指定する場所に別の属性付き文字列を挿入する |
| -(void)replaceCharactersInRange:(NSRange)aRange withString:(NSString *)aString | 変更可能な属性付き文字列の指定した範囲を文字列に置き換える |
| -(void)setAttributedString:(NSAttributedString *)attributedString | 変更可能な属性付き文字列を設定する |
| -(void)beginEditing | endEdtingとペアで、編集を開始する事を伝える |
| -(void)endEditing | beginEditingとペアで、編集を終了する事を伝える |
指定できる属性は以下の通り(他にもあるかも)。
| 属性名 | 意味 |
| NSFontAttributeName | フォント属性 |
| NSForegroundColorAttributeName | 文字の色 |
| NSBackgroundColorAttributeName | 文字の背景色 |
| NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName | 下線 |
| NSSuperscriptAttributeName | 上付き |
| NSBaselineOffsetAttributeName | ベースラインからのオフセット(±) |
| NSKernAttributeName | カーニング=文字間隔調整(±) |
| NSLigatureAttributeName | 組文字 |
| NSParagraphStyleAttributeName | 文字列が長いときに一部省略する |
| NSAttachmentAttributeName | ? |
- (void)drawRect
{
NSPoint point = { 10, 10 }; // NSPointは座標を示す構造体
NSMutableAttributedString* str = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc]initWithString:@"How's about your Mac? It's fine!"];
// フォントスタイル
[str addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName
value:[NSFont fontWithName:@"Chicago" size:36.0]
range:NSMakeRange(0,5)];
[str addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName
value:[NSFont fontWithName:@"Helvetica" size:24.0]
range:NSMakeRange(6,5)];
[str addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName
value:[NSFont fontWithName:@"Sand" size:12.0]
range:NSMakeRange(12,4)];
[str addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName
value:[NSFont fontWithName:@"Monaco" size:48.0]
range:NSMakeRange(17,4)];
[str addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName
value:[NSFont fontWithName:@"Apple Chancery" size:36.0]
range:NSMakeRange(22,4)];
[str addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName
value:[NSFont fontWithName:@"Times" size:48.0]
range:NSMakeRange(27,4)];
// 下線
[str addAttribute:NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName
value:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:1.0]
range:NSMakeRange(0,2)];
[str addAttribute:NSUnderlineStyleAttributeName
value:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:2.0]
range:NSMakeRange(2,3)];
// 文字色
[str addAttribute:NSForegroundColorAttributeName
value:[NSColor redColor]
range:NSMakeRange(6,5)];
[str addAttribute:NSForegroundColorAttributeName
value:[NSColor colorWithCalibratedWhite:0.0 alpha:0.3]
range:NSMakeRange(17,4)];
// 文字背景色
[str addAttribute:NSBackgroundColorAttributeName
value:[NSColor blueColor]
range:NSMakeRange(22,4)];
// 組文字
[str addAttribute:NSLigatureAttributeName
value:[NSNumber numberWithInt:1]
range:NSMakeRange(27,4)];
// カーニング
[str addAttribute:NSKernAttributeName
value:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:10.0]
range:NSMakeRange(22,4)];
// 上付き
[str addAttribute:NSSuperscriptAttributeName
value:[NSNumber numberWithInt:1]
range:NSMakeRange(17,4)];
// ベースラインからのオフセット
[str addAttribute:NSBaselineOffsetAttributeName
value:[NSNumber numberWithFloat:-10.0]
range:NSMakeRange(12,4)];
// 表示
[str drawAtPoint:point];
}
文字列内スキャン;NSScanner/NSCharacterSet
NSScannerは文字列の中を「スキャン」するクラスである。
名前からして「スキャナーに関するクラスか?」と思っていたが、全然違っていた。 日本語にすると「走査」となり、文字列中を検索すると思えば、ほぼ正しい。
NSScanner
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| +(id)scannerWithString:(NSString *)aString -(id)initWithString:(NSString *)aString | スキャン文字列を初期化して返す |
| -(void)setScanLocation:(NSUInteger)index | スキャン文字列のスキャンし始める文字位置を設定する |
| -(NSUInteger)scanLocation | スキャン文字列のスキャンし始める文字位置を返す |
| -(NSString *)string | スキャン文字列をNSString文字列で返す |
| -(void)setCaseSensitive:(BOOL)flag | 探す文字の大文字と小文字を区別するかを設定する |
| -(BOOL)caseSensitive | 探す文字の大文字と小文字を区別するかを返す |
| -(void)setCharactersToBeSkipped:(NSCharacterSet *)skipSet | スキップしたい文字列を設定する |
| -(NSCharacterSet *)charactersToBeSkipped | スキャン文字列が無視する文字の文字セットを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanCharactersFromSet:(NSCharacterSet *)scanSet intoString:(NSString **)stringValue | スキャン文字列を探す |
| -(BOOL)scanUpToCharactersFromSet:(NSCharacterSet *)stopSet intoString:(NSString **)stringValue | スキャン文字列中に指定した文字群があるかを調べる |
| -(BOOL)scanString:(NSString *)string intoString:(NSString **)stringValue | スキャン文字列に指定した文字列が含まれるかを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanUpToString:(NSString *)stopString intoString:(NSString **)stringValue | スキャン文字列に指定した文字列があるかを返す |
| -(BOOL)isAtEnd | スキャン文字列を最後までスキャンしたかを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanDecimal:(NSDecimal *)decimalValue | スキャン文字列がBCDかどうかを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanDouble:(double *)doubleValue | スキャン文字列が倍精度浮動小数点数値かを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanFloat:(float *)floatValue | スキャン文字列が浮動小数点数値かを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanInt:(int *)intValue | スキャン文字列が整数値かを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanHexInt:(unsigned *)intValue | スキャン文字列が16進数値かを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanHexLongLong:(unsigned long long *)result | スキャン文字列がlong long16進数値かを返す |
| -(BOOL)scanLongLong:(long long *)longLongValue: | スキャン文字列がlong long数値かを返す |
| +(id)localizedScannerWithString:(NSString *)aString | ローカライズされた文字でスキャン文字列を返す |
| -(void)setLocale:(id)aLocale | スキャン文字列の文字ロケールを辞書で設定する |
| -(id)locale | スキャン文字列のロケールを辞書で返す |
NSScannerを使うときには、NSCharacterSetによる文字セットの設定が必ず対になる。
NSCharacterSet
| メソッド名 | 動作 |
| +(id)symbolCharacterSet | シンボルキャラクタセットを返す |
| +(id)alphanumericCharacterSet | アルファベットの文字セットを返す |
| +(id)controlCharacterSet | コントロール文字のセットを返す |
| +(id)decimalDigitCharacterSet | 数字の文字セットを返す |
| +(id)decomposableCharacterSet | ユニコード1.1でアクセント記号のついた文字セットを返す |
| +(id)illegalCharacterSet | 例外の文字セットを返す |
| +(id)letterCharacterSet | アルファベットの文字セットを返す |
| +(id)lowercaseLetterCharacterSet | 小文字のアルファベットの文字セットを返す |
| +(id)nonBaseCharacterSet | ベース文字でない文字セットを返す |
| +(id)uppercaseLetterCharacterSet | 大文字のみを含んでいる文字セットを返す |
| +(id)whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet | スペースとタブとCRだけを含んでいる文字セットを返す |
| +(id)whitespaceCharacterSet | スペースとタブだけを含んでいる文字セットを返す |
| +(id)characterSetWithBitmapRepresentation:(NSData *)data | バイナリデータから文字セットを作る |
| +(id)characterSetWithCharactersInString:(NSString *)aString | 指定した文字列から文字セットを作る |
| +(id)characterSetWithContentsOfFile:(NSString *)path | 指定した指定パスのファイル中文字列から文字セットを作る |
| +(id)characterSetWithRange:(NSRange)aRange | 指定した範囲のユニコード文字で文字セットを作る |
| -(BOOL)characterIsMember:(unichar)aCharacter | 指定した文字は文字セットのメンバーかを返す |
| -(BOOL)hasMemberInPlane:(uint8_t)thePlane | 指定した面は文字セットのメンバーを含むかを返す |
| -(BOOL)isSupersetOfSet:(NSCharacterSet *)theOtherSet | 指定した文字セットは、レシーバの文字セットのスーパーセットかを返す |
| -(BOOL)longCharacterIsMember:(UTF32Char)theLongChar | 指定した文字は文字セットのメンバーかを返す |
| -(NSCharacterSet *)invertedSet | レシーバに含まれていない文字だけを含んでいる文字セットを返す |
| -(NSData *)bitmapRepresentation | 文字セットのバイナリ形式データを返す |
scanCharactersFromSet: intoString: は、指定されたNSCharacterSetの「文字が出ている限り」調べを進める。 scanUpToCharactersFromSet:intoString: は、NSCharacterSet の「文字が出て来るまで」調べる。 この2つを利用してトークン分割を書くと、以下のようになる。 スキャン対象文字列は、操作処理されるたびに内部のポインターが進む。なので、繰り返し呼び出すことで 順次処理が出来る。
NSCharacterSet* chSet;
NSString* scannedName;
NSScanner* scanner;
string = @"abc, def,gh, ijk";
chSet = [NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@", "]; // 分割区切り文字(デリミタ)
scanner = [NSScanner scannerWithString:string]; // スキャン用文字列を作成
while(![scanner isAtEnd]) { // 終端まで
// まず区切り文字が出てくるまで探す
// intoStringには区切り文字直前までの文字が入る
if([scanner scanUpToCharactersFromSet:chSet intoString:&scannedName]) {
NSLog(scannedName);
}
// 区切り文字そのものを飛ばす
// 区切り文字の取り出しは不要なので、intoStringにはnilを指定している
[scanner scanCharactersFromSet:chSet intoString:nil];
}
NSScanner *scanString = [[NSScanner alloc] initWithString: @"abcdefg hilklmn opqrstu" ];
NSCharacterSet *cSet = [[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString: @"1234567890abcdfeABCDEF"] retain];
NSString *name;
[scanString setScanLocation: 1];
if ([scanString scanCharactersFromSet:cSet intoString:&name]) {
NSLog( @"YES" );
NSLog(name);
} else {
NSLog( @"NO" );
}
NSStringのcomponentsSeparatedByStringとの違いは、一括処理して配列に入れるか順次処理するかである。まあ、同じようなメソッドがあちこちにあるのはここだけの話ではないので、 少しでも目的に近い方を使うべきなのだろう。もしくはワークエリアのサイズと相談とか (配列を作るとそれだけワークを必要とするから)。